ANSI FLANGE PRESSURE RATING EXPLAINED
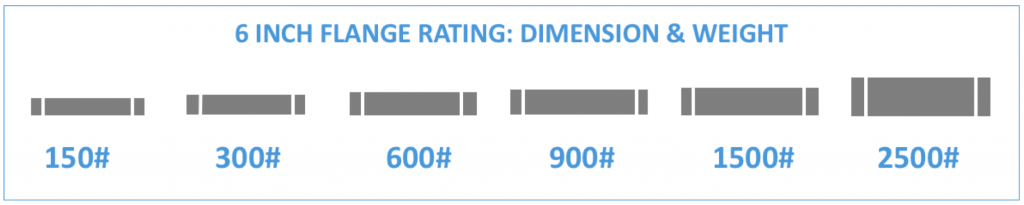
Now consider what this means in terms of pressure rating:
At a temperature of 600 degrees F°, the class 150 flange can sustain only 140 psi (as per the rating chart below)
The class 300 flange (which is larger and stronger but has the same hole size) can sustain 570 psi at 600 degrees F°.
Finally, a class 2500 flange of the same size can withstand 34 times the pressure of a class 150 flange, with a rating of 4730 psi at 600 F°!
Scroll down to see the rating table that pertains to your flange (this depends on the material of the flange, as flanges with different material grades have different pressure ratings)
Determine your piping system’s maximum working temperature (i.e. select one line in the table)
Choose a rating based on the expected maximum pressure at that temperature level (i.e. select one column in that line)
You’ve now received the required rating!
Below are the ASME B16.34 pressure rating charts for the most common flange materials to assist you (carbon, alloy, stainless).
Pressure rating is the highest amount of pressure that a flange can handle as the temperature rises. The ANSI/ASME B16.5 standard lists seven pressure ratings for flanges: 150, 300, 400, 600, 900, 1500, and 2500.
The terms “pressure rating,” “class,” “#,” “Lb,” and “Lbs” all mean the same thing when it comes to how a flange handles pressure and temperature (and other equipment like valves, fittings, etc).
Let’s use an example to make this clear:
If two flanges have the same bore size, say 6 inches, and the same material, say A105, but different pressure ratings, say class 150 and class 300, the class 150 flange will be smaller, lighter, and less sturdy than the class 300 flange (class 300). This is what the picture shows:
How the Flange Rating System Works
People who are new to the pipe industry frequently have difficulty understanding how flange rating works. Let us first define a flange and the role it plays in the plumbing sector before proceeding with the discussion.
What exactly is a flange and how does it work?
A flange is a piece of equipment that connects pipes, pumps, valves, and other piping components to form a pipeline system. The flange is an important part of the piping system because it allows for easier cleaning, inspection, and modification. Weld Neck Flange, Slip-on Flange, Socket Weld Flanges, Lap Joint Flange, Threaded flange, Blind flange, Orifice flanges, Reducing flanges, and many other types of flanges are available.
What is the flange rating and how does it work?
It’s crucial to make sure that the flanges used in the oil, gas, and petrochemical industries can resist the pressures and temperatures they’re exposed to. Not only is the size of the flanges significant, but so is the rating. As a result, selecting a flange with the appropriate rating ensures that it can endure the pressures of functioning at different temperatures.
The maximum pressure that a flange can withstand at high or increasing temperatures is defined by the class of the flange. Flanges having a higher flange rating or flange class are naturally considered stronger since they can withstand more pressure at higher temperatures.
The ASME B16.5 standard, which applies to flanged fittings and pipe flanges, is the industry standard for flanges. This contains flanges with diameters ranging from 12″ NPS to 24″ NPS.
As a result, as the temperature rises, the maximum allowable pressure falls. With the following example, the notion of flange rating can be readily described.
A Class 300 flange can resist higher pressure than a Class 150 flange because it is made of more metal and can tolerate more pressure. However, a flange’s pressure capability is affected by a number of factors.
Because it is comprised of more metal and can withstand more pressure, a Class 300 flange can withstand higher pressure than a Class 150 flange. The pressure capability of a flange, on the other hand, is influenced by a variety of elements.
CARBON STEEL FLANGE RATING CHART

ANSI FLANGE ASTM A105, A350 Gr. LF2/LF6 Class 1
The maximum pressure for flanges of classes 150/300/400/600/900/1500/2500 at increasing temperatures (Celsius or Fahrenheit) – in PSI – is shown in the flange rating table.
| ANSI/ASME B16.34 | ANSI PRESSURE RATING | ||||||
| Temperature (in F°) | 150# | 300# | 400# | 600# | 900# | 1500# | 2500# |
| < 100 | 285 | 740 | 985 | 1480 | 2220 | 3705 | 6170 |
| 200 | 260 | 680 | 905 | 1360 | 2035 | 3395 | 5655 |
| 300 | 230 | 655 | 870 | 1310 | 1965 | 3270 | 5450 |
| 400 | 200 | 635 | 845 | 1265 | 1900 | 3170 | 5280 |
| 500 | 170 | 605 | 805 | 1205 | 1810 | 3015 | 5025 |
| 600 | 140 | 570 | 755 | 1135 | 1705 | 2840 | 4730 |
| 650 | 125 | 550 | 730 | 1100 | 1650 | 2745 | 4575 |
| 700 | 110 | 530 | 710 | 1060 | 1590 | 2655 | 4425 |
| 750 | 95 | 505 | 675 | 1015 | 1520 | 2535 | 4230 |
| 800 | 80 | 410 | 550 | 825 | 1235 | 2055 | 3430 |
| 850 | 65 | 320 | 425 | 640 | 955 | 1595 | 2655 |
| 900 | 50 | 230 | 305 | 460 | 690 | 1150 | 1915 |
| 950 | 35 | 135 | 185 | 275 | 410 | 685 | 1145 |
| 1000 | 20 | 85 | 115 | 170 | 255 | 430 | 715 |
| Hydrostatic Test Pressure (in Psig) | 450 | 1125 | 1500 | 2225 | 3350 | 5575 | 9275 |
Notes
The maximum pressure for flanges of classes 150/300/400/600/900/1500/2500 at increasing temperatures (Celsius or Fahrenheit) – in bars – is shown in the flange rating table.
| ANSI/ASME B16.34 | ANSI PRESSURE RATING | ||||||
| Temperature in C° | 150# | 300# | 400# | 600# | 900# | 1500# | 2500# |
| -29 / 38 | 19.6 | 51.1 | 68.1 | 102.1 | 153.2 | 255.3 | 425.5 |
| 50 | 19.2 | 50.1 | 66.8 | 100.2 | 150.4 | 250.6 | 417.7 |
| 100 | 17.7 | 46.6 | 62.1 | 93.2 | 139.8 | 233 | 388.3 |
| 150 | 15.8 | 45.1 | 60.1 | 90.2 | 135.2 | 225.4 | 375.6 |
| 200 | 13.8 | 43.8 | 58.4 | 87.6 | 131.4 | 219 | 365 |
| 250 | 12.1 | 41.9 | 55.9 | 83.9 | 125.8 | 209.7 | 349.5 |
| 300 | 10.2 | 39.8 | 53.1 | 79.6 | 119.5 | 199.1 | 331.8 |
| 325 | 9.3 | 38.7 | 51.6 | 77.4 | 116.1 | 193.6 | 322.6 |
| 350 | 8.4 | 37.6 | 50.1 | 75.1 | 112.7 | 187.8 | 313 |
| 375 | 7.4 | 36.4 | 48.5 | 72.7 | 109.1 | 181.8 | 303.1 |
| 400 | 6.5 | 34.7 | 46.3 | 69.4 | 104.2 | 173.6 | 289.3 |
| 425 | 5.5 | 28.8 | 38.4 | 57.5 | 86.3 | 143.8 | 239.7 |
| 450 | 4.6 | 23 | 30.7 | 46 | 69 | 115 | 191.7 |
| 475 | 3.7 | 17.4 | 23.2 | 34.9 | 52.3 | 87.2 | 145.3 |
| 500 | 2.8 | 11.8 | 15.7 | 23.5 | 35.3 | 58.8 | 97.9 |
Notes:
ASTM A105: Long-term exposure to temperatures above 425°C transforms steel’s carbide phase to graphite (this material is not recommended for consistent temperatures above this number).
The ASTM A350 LF6 standard states that it should not be utilized at temperatures above 260 degrees Celsius.
ANSI FLANGE ASTM A350 Gr. LF3, A350 LF6, Class 2
The flange rating chart depicts the maximum pressure for flanges of classes 150/300/400/600/900/1500/2500 at various temperatures (in degrees Celsius or Fahrenheit) – in PSI.
| ANSI/ASME B16.34 | ANSI PRESSURE RATING | ||||||
| Temperature in °F | 150# | 300# | 400# | 600# | 900# | 1500# | 2500# |
| -20 to 100 | 290 | 750 | 1000 | 1500 | 2250 | 3750 | 6250 |
| 200 | 260 | 750 | 1000 | 1500 | 2250 | 3750 | 6250 |
| 300 | 230 | 730 | 970 | 1455 | 2185 | 3640 | 6070 |
| 400 | 200 | 705 | 940 | 1410 | 2115 | 3530 | 5880 |
| 500 | 170 | 665 | 885 | 1330 | 1995 | 3325 | 5540 |
| 600 | 140 | 605 | 805 | 1210 | 1815 | 3025 | 5040 |
| 650 | 125 | 590 | 785 | 1175 | 1765 | 2940 | 4905 |
| 700 | 110 | 570 | 755 | 1135 | 1705 | 2840 | 4730 |
| 750 | 95 | 505 | 670 | 1010 | 1510 | 2520 | 4200 |
| 800 | 80 | 410 | 550 | 825 | 1235 | 2060 | 3430 |
| 850 | 65 | 270 | 355 | 535 | 805 | 1340 | 2230 |
| 900 | 50 | 170 | 230 | 345 | 515 | 860 | 1430 |
| 950 | 35 | 105 | 140 | 205 | 310 | 515 | 860 |
| 1000 | 20 | 50 | 70 | 105 | 155 | 260 | 430 |
ANSI FLANGE ASTM A350 Gr. LF1
The maximum pressure for flanges of classes 150/300/400/600/900/1500/2500 at increasing temperatures (Celsius or Fahrenheit) — in PSI — is shown in the flange rating table.
| ANSI/ASME B16.34 | ANSI PRESSURE RATING | ||||||
| Temperature °F | 150# | 300# | 400# | 600# | 900# | 1500# | 2500# |
| -20 to 100 | 235 | 620 | 825 | 1235 | 1850 | 3085 | 1545 |
| 200 | 215 | 560 | 750 | 1125 | 1685 | 2810 | 4680 |
| 300 | 210 | 550 | 730 | 1095 | 1640 | 2735 | 4560 |
| 400 | 200 | 530 | 705 | 1060 | 1585 | 2645 | 4405 |
| 500 | 170 | 500 | 665 | 995 | 1495 | 2490 | 4150 |
| 600 | 140 | 455 | 610 | 915 | 1370 | 2285 | 3805 |
| 650 | 125 | 450 | 600 | 895 | 1345 | 2245 | 3740 |
| 700 | 110 | 450 | 600 | 895 | 1345 | 2245 | 3740 |
| 750 | 95 | 445 | 590 | 885 | 1325 | 2210 | 3685 |
| 800 | 80 | 370 | 495 | 740 | 1110 | 1850 | 3085 |
| 850 | 65 | 270 | 355 | 535 | 805 | 1340 | 2230 |
| 900 | 50 | 170 | 230 | 345 | 515 | 860 | 1430 |
| 950 | 35 | 105 | 140 | 205 | 310 | 515 | 860 |
| 1000 | 20 | 50 | 70 | 105 | 155 | 260 | 430 |
ALLOY STEEL FLANGE RATING CHART

ANSI FLANGE ASTM A182 Gr. F1 (Chrome Moly)
The maximum pressure for flanges of classes 150/300/400/600/900/1500/2500 at increasing temperatures (in Celsius or Fahrenheit) – in PSI – is shown in the flange rating table.
| ANSI/ASME B16.34 | ANSI PRESSURE RATING | ||||||
| Temperature °F | 150# | 300# | 400# | 600# | 900# | 1500# | 2500# |
| -20 to 100 | 265 | 695 | 925 | 1390 | 2085 | 3470 | 5785 |
| 200 | 260 | 680 | 905 | 1360 | 2035 | 3395 | 5660 |
| 300 | 230 | 655 | 870 | 1305 | 1955 | 3260 | 5435 |
| 400 | 200 | 640 | 855 | 1280 | 1920 | 3200 | 5330 |
| 500 | 170 | 620 | 830 | 1245 | 1865 | 3105 | 5180 |
| 600 | 140 | 605 | 805 | 1210 | 1815 | 3025 | 5040 |
| 650 | 125 | 590 | 785 | 1175 | 1765 | 2940 | 4905 |
| 700 | 110 | 570 | 755 | 1135 | 1705 | 2840 | 4730 |
| 750 | 95 | 530 | 710 | 1065 | 1595 | 2660 | 4430 |
| 800 | 80 | 510 | 675 | 1015 | 1525 | 2540 | 4230 |
| 850 | 65 | 485 | 650 | 975 | 1460 | 2435 | 4060 |
| 900 | 50 | 450 | 600 | 900 | 1350 | 2245 | 3745 |
| 950 | 35 | 280 | 375 | 560 | 845 | 1405 | 2345 |
| 1000 | 20 | 165 | 220 | 330 | 495 | 825 | 1370 |
STAINLESS STEEL FLANGE RATING CHART

ANSI FLANGE ASTM A182 Gr. F304, 304L
The maximum pressure for flanges of classes 150/300/400/600/900/1500/2500 at increasing temperatures (Celsius or Fahrenheit) – in PSI – is shown in the flange rating table.
| ANSI/ASME B16.34 | ANSI PRESSURE RATING | ||||||
| Temperature °F | 150# | 300# | 400# | 600# | 900# | 1500# | 2500# |
| -20 to 100 | 275 | 720 | 960 | 1440 | 2160 | 3600 | 6000 |
| 200 | 230 | 600 | 800 | 1200 | 1800 | 3000 | 5000 |
| 300 | 205 | 540 | 720 | 1080 | 1620 | 2700 | 4500 |
| 400 | 190 | 495 | 660 | 995 | 1490 | 2485 | 4140 |
| 500 | 170 | 465 | 620 | 930 | 1395 | 2330 | 3880 |
| 600 | 140 | 435 | 580 | 875 | 1310 | 2185 | 3640 |
| 650 | 125 | 430 | 575 | 860 | 1290 | 2150 | 3580 |
| 700 | 110 | 425 | 565 | 850 | 1275 | 2125 | 3540 |
| 750 | 95 | 415 | 555 | 830 | 1245 | 2075 | 3460 |
| 800 | 80 | 405 | 540 | 805 | 1210 | 2015 | 3360 |
| 850 | 65 | 395 | 530 | 790 | 1190 | 1980 | 3300 |
| 900 | 50 | 390 | 520 | 780 | 1165 | 1945 | 3240 |
| 950 | 35 | 380 | 510 | 765 | 1145 | 1910 | 3180 |
| 1000 | 20 | 320 | 430 | 640 | 965 | 1605 | 2675 |
| 1050 | 20 | 310 | 410 | 615 | 925 | 1545 | 2570 |
| 1100 | 20 | 255 | 345 | 515 | 770 | 1285 | 2145 |
| 1150 | 20 | 200 | 265 | 400 | 595 | 995 | 1655 |
| 1200 | 20 | 155 | 205 | 310 | 465 | 770 | 1285 |
| 1250 | 20 | 115 | 150 | 225 | 340 | 565 | 945 |
| 1300 | 20 | 85 | 115 | 170 | 255 | 430 | 715 |
| 1350 | 20 | 60 | 80 | 125 | 185 | 310 | 515 |
| 1400 | 20 | 50 | 65 | 95 | 145 | 240 | 400 |
| 1450 | 15 | 35 | 45 | 70 | 105 | 170 | 285 |
| 1500 | 10 | 25 | 35 | 55 | 80 | 135 | 230 |
The maximum pressure for flanges of classes 150/300/400/600/900/1500/2500 at increasing temperatures (Celsius or Fahrenheit) – in PSI – is shown in the flange rating table.
| ANSI/ASME B16.34 | ANSI PRESSURE RATING | ||||||
| Temperature °F | 150# | 300# | 400# | 600# | 900# | 1500# | 2500# |
| -20 to 100 | 275 | 720 | 960 | 1440 | 2160 | 3600 | 6000 |
| 200 | 235 | 620 | 825 | 1240 | 1860 | 3095 | 5160 |
| 300 | 215 | 560 | 745 | 1120 | 1680 | 2795 | 4660 |
| 400 | 195 | 515 | 685 | 1025 | 1540 | 2570 | 4280 |
| 500 | 170 | 480 | 635 | 955 | 1435 | 2390 | 3980 |
| 600 | 140 | 450 | 600 | 900 | 1355 | 2255 | 3760 |
| 650 | 125 | 445 | 590 | 890 | 1330 | 2220 | 3700 |
| 700 | 110 | 430 | 580 | 870 | 1305 | 2170 | 3620 |
| 750 | 95 | 425 | 570 | 855 | 1280 | 2135 | 3560 |
| 800 | 80 | 420 | 565 | 845 | 1265 | 2110 | 3520 |
| 850 | 65 | 420 | 555 | 835 | 1255 | 2090 | 3480 |
| 900 | 50 | 415 | 555 | 830 | 1245 | 2075 | 3460 |
| 950 | 35 | 385 | 515 | 775 | 1160 | 1930 | 3220 |
| 1000 | 20 | 350 | 465 | 700 | 1050 | 1750 | 2915 |
| 1050 | 20 | 345 | 460 | 685 | 1030 | 1720 | 2865 |
| 1100 | 20 | 305 | 405 | 610 | 915 | 1525 | 2545 |
| 1150 | 20 | 235 | 315 | 475 | 710 | 1185 | 1970 |
| 1200 | 20 | 185 | 245 | 370 | 555 | 925 | 1545 |
| 1250 | 20 | 145 | 195 | 295 | 440 | 735 | 1230 |
| 1300 | 20 | 115 | 155 | 235 | 350 | 585 | 970 |
| 1350 | 20 | 95 | 130 | 190 | 290 | 480 | 800 |
| 1400 | 20 | 75 | 100 | 150 | 225 | 380 | 630 |
| 1450 | 20 | 60 | 80 | 115 | 175 | 290 | 485 |
| 1500 | 20 | 40 | 55 | 85 | 125 | 205 | 345 |
Read More :
What you should know about forged threaded fittings: Forged Threaded 45-degree Elbows are said to be one of the oldest types of forged fittings that have been used for a long time. When pipes have a smaller bore and diameter, threaded fittings are used to connect them. A pipe with a threaded fitting should have a nominal diameter of around 2 NPS or less.
What Can The SS 904L Tube Do Reduce Air Pollution? : This high-alloy austenitic stainless steel tube is a popular choice because it works well in our climate and can also be used in harsh environments.

